源码阅读准备
- 下载Apache Hadoop-2.9.2官方源码
- 将源码导入idea中
启动idea在提示界面选择导入
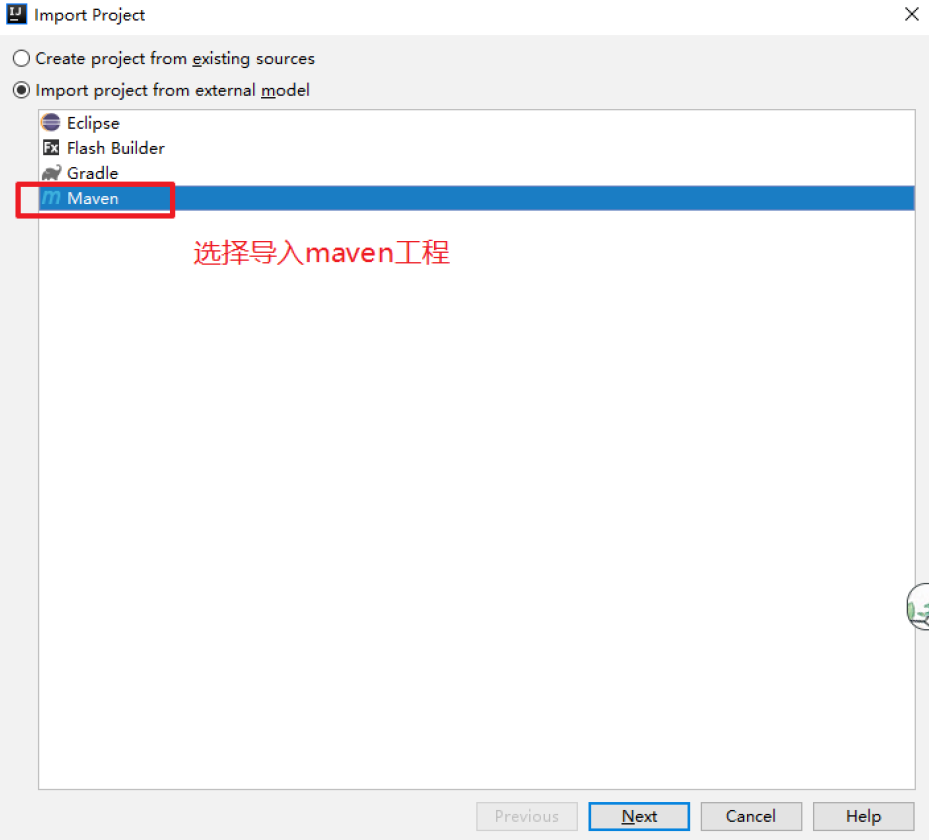
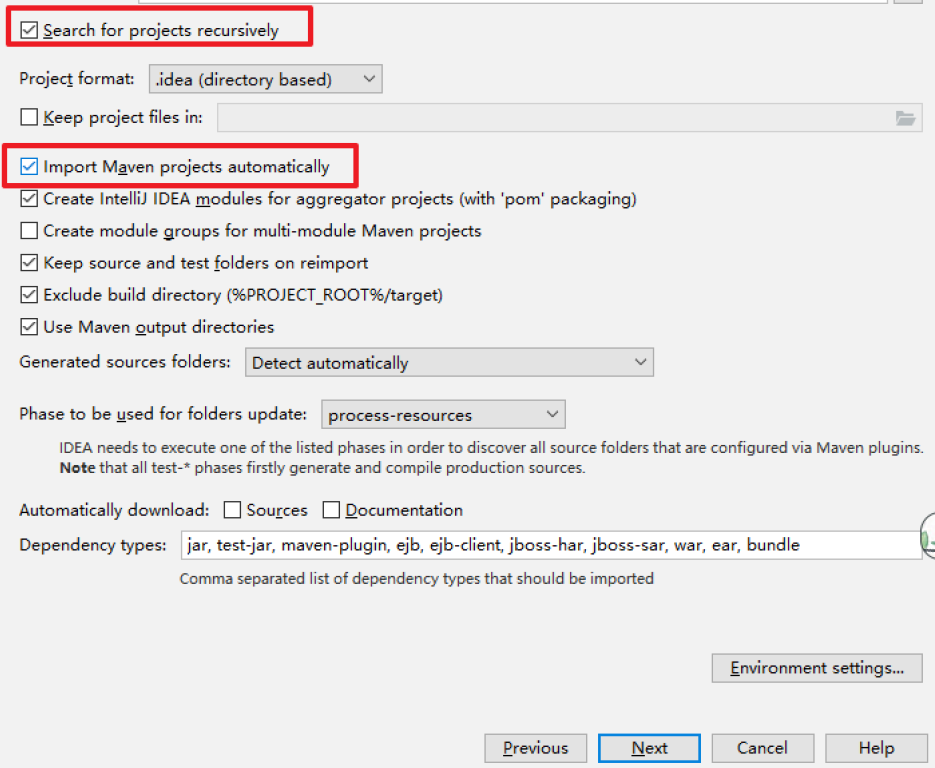
点击Finish
等待下载和解决依赖完成,源码导入成功!!
NameNode 启动流程
命令启动Hdfs集群
start-dfs.sh
该命令会启动Hdfs的NameNode以及DataNode,启动NameNode主要是通过org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.server.namenode.NameNode类。
重点关注NameNode在启动过程中做了哪些工作(偏离主线的技术细节不深究)
对于分析启动流程主要关注两部分代码:
public class NameNode extends ReconfigurableBase implements NameNodeStatusMXBean {
//该静态代码块主要是初始化一些HDFS的配置信息
static{
HdfsConfiguration.init();
//进入之后发现方法是空的,没有任何操作?其实不是观察HdfsConfiguration的静态代码块
}
//HdfsConfiguration的类以及静态代码块
public class HdfsConfiguration extends Configuration {
static {
addDeprecatedKeys();
// adds the default resources
Configuration.addDefaultResource("hdfs-default.xml");
Configuration.addDefaultResource("hdfs-site.xml");
}
...
//main方法
public static void main(String argv[]) throws Exception{
//分析传入的参数是否为帮助参数,如果是帮助的话打印帮助信息,并退出。
if(DFSUtil.parseHelpArgument(argv,NameNode.USAGE,System.out,true)){
System.exit(0);
}
try{
//格式化输出启动信息,并且创建hook(打印节点关闭信息)
StringUtils.startupShutdownMessage(NameNode.class,argv,LOG);
//创建namenode
NameNode namenode=createNameNode(argv,null);
if(namenode!=null){
//加入集群
namenode.join();
}
}
catch(Throwable e){
//异常处理
LOG.error("Failed to start namenode.",e);
terminate(1,e);
}
}
----------------------------------------------------------------------
//关注createNameNode
public static NameNode createNameNode(String argv[], Configuration conf) throws IOException {
LOG.info("createNameNode " + Arrays.asList(argv));
if (conf == null)
conf = new HdfsConfiguration();
// Parse out some generic args into Configuration.
GenericOptionsParser hParser = new GenericOptionsParser(conf, argv);
argv = hParser.getRemainingArgs();
// Parse the rest, NN specific args.
//解析启动的参数
StartupOption startOpt = parseArguments(argv);
if (startOpt == null) {
printUsage(System.err);
return null;
}
setStartupOption(conf, startOpt);
switch (startOpt) {
....
default: {
//正常启动进入该分支
//初始化metric系统
DefaultMetricsSystem.initialize("NameNode");
//返回新的NameNode
return new NameNode(conf);
}
}
}
----------------------------------------------------------------------
//NameNode的构造
public NameNode(Configuration conf) throws IOException {
this(conf, NamenodeRole.NAMENODE);
}
...
protected NameNode(Configuration conf, NamenodeRole role) throws IOException {
this.conf = conf;
this.role = role;
// 设置NameNode#clientNamenodeAddress为"hdfs://localhost:9000"
setClientNamenodeAddress(conf);
String nsId = getNameServiceId(conf);
String namenodeId = HAUtil.getNameNodeId(conf, nsId);
// HA相关
this.haEnabled = HAUtil.isHAEnabled(conf, nsId);
state = createHAState(getStartupOption(conf));
this.allowStaleStandbyReads = HAUtil.shouldAllowStandbyReads(conf);
this.haContext = createHAContext();
try {
initializeGenericKeys(conf, nsId, namenodeId);
// 完成实际的初始化工作
initialize(conf);
// HA相关
try {
haContext.writeLock();
state.prepareToEnterState(haContext);
state.enterState(haContext);
}
finally {
haContext.writeUnlock();
}
}
catch (IOException e) {
this.stop();
throw e;
}
catch (HadoopIllegalArgumentException e) {
this.stop();
throw e;
}
}
//尽管本地没有开启HA(haEnabled=false**),**namenode依然拥有一个HAState,namenode的HAState状态为active.
----------------------------------------------------------------------
// 完成实际的初始化工作
// initialize(conf);
protected void initialize(Configuration conf) throws IOException {
if (conf.get(HADOOP_USER_GROUP_METRICS_PERCENTILES_INTERVALS) == null) {
String intervals = conf.get(DFS_METRICS_PERCENTILES_INTERVALS_KEY);
if (intervals != null) {
conf.set(HADOOP_USER_GROUP_METRICS_PERCENTILES_INTERVALS, intervals);
}
}
UserGroupInformation.setConfiguration(conf);
loginAsNameNodeUser(conf);
// 初始化metric
NameNode.initMetrics(conf, this.getRole());
StartupProgressMetrics.register(startupProgress);
// 启动httpServer
if (NamenodeRole.NAMENODE == role) {
startHttpServer(conf);
}
this.spanReceiverHost = SpanReceiverHost.getInstance(conf);
// 从namenode目录加载fsimage与editlog,初始化FsNamesystem、FsDirectory、LeaseManager等
loadNamesystem(conf);
// 创建RpcServer,封装了NameNodeRpcServer clientRpcServer,支持ClientNamenodeProtocol、DatanodeProtocolPB等协议
rpcServer = createRpcServer(conf);
if (clientNamenodeAddress == null) {
// This is expected for MiniDFSCluster. Set it now using
// the RPC server's bind address.
clientNamenodeAddress = NetUtils.getHostPortString(rpcServer.getRpcAddress());
LOG.info("Clients are to use " + clientNamenodeAddress + " to access" + " this namenode/service.");
}
if (NamenodeRole.NAMENODE == role) {
httpServer.setNameNodeAddress(getNameNodeAddress());
httpServer.setFSImage(getFSImage());
}
// 启动JvmPauseMonitor等,反向监控JVM
pauseMonitor = new JvmPauseMonitor(conf);
pauseMonitor.start();
metrics.getJvmMetrics().setPauseMonitor(pauseMonitor);
// 启动执行多个非常重要工作的多个线程
startCommonServices(conf);
}
----------------------------------------------------------------------
private void startCommonServices(Configuration conf) throws IOException {
// 创建NameNodeResourceChecker、激活BlockManager等
namesystem.startCommonServices(conf, haContext);
registerNNSMXBean();
// 角色非`NamenodeRole.NAMENODE`的在此处启动HttpServer
if (NamenodeRole.NAMENODE != role) {
startHttpServer(conf);
httpServer.setNameNodeAddress(getNameNodeAddress());
httpServer.setFSImage(getFSImage());
}
// 启动RPCServer
rpcServer.start();
...// 启动各插件
LOG.info(getRole() + " RPC up at: " + rpcServer.getRpcAddress());
if (rpcServer.getServiceRpcAddress() != null) {
LOG.info(getRole() + " service RPC up at: " + rpcServer.getServiceRpcAddress());
}
}
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void startCommonServices(Configuration conf, HAContext haContext) throws IOException {
this.registerMBean();
// register the MBean for the FSNamesystemState
writeLock();
this.haContext = haContext;
try {
// 创建NameNodeResourceChecker,并立即检查一次
nnResourceChecker = new NameNodeResourceChecker(conf);
checkAvailableResources();
assert safeMode != null && !isPopulatingReplQueues();
// 设置一些启动过程中的信息
StartupProgress prog = NameNode.getStartupProgress();
prog.beginPhase(Phase.SAFEMODE);
prog.setTotal(Phase.SAFEMODE, STEP_AWAITING_REPORTED_BLOCKS, getCompleteBlocksTotal());
// 设置已完成的数据块总量
setBlockTotal();
// 激活BlockManager
blockManager.activate(conf);
}
finally {
writeUnlock();
}
registerMXBean();
DefaultMetricsSystem.instance().register(this);
snapshotManager.registerMXBean();
}
//blockManager.activate(conf)激活BlockManager主要完成PendingReplicationMonitor、DecommissionManager#Monitor、HeartbeatManager#Monitor、ReplicationMonitor
public void activate(Configuration conf) {
// 启动PendingReplicationMonitor
pendingReplications.start();
// 激活DatanodeManager:启动DecommissionManager--Monitor、HeartbeatManager--Monitor
datanodeManager.activate(conf);
// 启动BlockManager--ReplicationMonitor
this.replicationThread.start();
}
namenode的主要责任是文件元信息与数据块映射的管理。相应的,namenode的启动流程需要关注与客户端、datanode通信的工作线程,文件元信息的管理机制,数据块的管理机制等。其中,RpcServer主要负责与客户端、datanode通信,FSDirectory主要负责管理文件元信息。
DataNode 启动流程
datanode的Main Class是DataNode,先找到DataNode.main()
public class DataNode extends ReconfigurableBase implements InterDatanodeProtocol, ClientDatanodeProtocol, TraceAdminProtocol, DataNodeMXBean, ReconfigurationProtocol {
public static final Logger LOG = LoggerFactory.getLogger(DataNode.class);
static{
HdfsConfiguration.init();
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
if (DFSUtil.parseHelpArgument(args, DataNode.USAGE, System.out, true)) {
System.exit(0);
}
secureMain(args, null);
}
...
public static void secureMain(String args[], SecureResources resources) {
int errorCode = 0;
try {
// 打印启动信息
StringUtils.startupShutdownMessage(DataNode.class, args, LOG);
// 完成创建datanode的主要工作
DataNode datanode = createDataNode(args, null, resources);
if (datanode != null) {
datanode.join();
} else {
errorCode = 1;
}
}
catch (Throwable e) {
LOG.fatal("Exception in secureMain", e);
terminate(1, e);
}
finally {
LOG.warn("Exiting Datanode");
terminate(errorCode);
}
}
---------------------------------------------------
public static DataNode createDataNode(String args[], Configuration conf, SecureResources resources) throws IOException {
// 完成大部分初始化的工作,并启动部分工作线程
DataNode dn = instantiateDataNode(args, conf, resources);
if (dn != null) {
// 启动剩余工作线程
dn.runDatanodeDaemon();
}
return dn;
}
--------------------------------------------------
/** Start a single datanode daemon and wait for it to finish.
* If this thread is specifically interrupted, it will stop waiting.
*/
public void runDatanodeDaemon() throws IOException {
// 在DataNode.instantiateDataNode()执行过程中会调用该方法(见后)
blockPoolManager.startAll();
dataXceiverServer.start();
if (localDataXceiverServer != null) {
localDataXceiverServer.start();
}
ipcServer.start();
startPlugins(conf);
}
--------------------------------------------------------
public static DataNode instantiateDataNode(String args [], Configuration conf, SecureResources resources) throws IOException {
if (conf == null)
conf = new HdfsConfiguration();
... // 参数检查等
Collection<StorageLocation> dataLocations = getStorageLocations(conf);
UserGroupInformation.setConfiguration(conf);
SecurityUtil.login(conf, DFS_DATANODE_KEYTAB_FILE_KEY, DFS_DATANODE_KERBEROS_PRINCIPAL_KEY);
return makeInstance(dataLocations, conf, resources);
}
--------------------------------------------------------------------
//DataNode.makeInstance()开始创建DataNode
static DataNode makeInstance(Collection<StorageLocation> dataDirs, Configuration conf, SecureResources resources) throws IOException {
...// 检查数据目录的权限
assert locations.size() > 0 : "number of data directories should be > 0";
return new DataNode(conf, locations, resources);
}
...
DataNode(final Configuration conf, final List<StorageLocation> dataDirs, final SecureResources resources) throws IOException {
super(conf);
...// 参数设置
try {
hostName = getHostName(conf);
LOG.info("Configured hostname is " + hostName);
startDataNode(conf, dataDirs, resources);
}
catch (IOException ie) {
shutdown();
throw ie;
}
}
...
void startDataNode(Configuration conf, List<StorageLocation> dataDirs, SecureResources resources) throws IOException {
...// 参数设置
// 初始化DataStorage
storage = new DataStorage();
// global DN settings
// 注册JMX
registerMXBean();
// 初始化DataXceiver(流式通信),DataNode runDatanodeDaemon()中启动
initDataXceiver(conf);
// 启动InfoServer(Web UI)
startInfoServer(conf);
// 启动JVMPauseMonitor(反向监控JVM情况,可通过JMX查询)
pauseMonitor = new JvmPauseMonitor(conf);
pauseMonitor.start();
...// 略
// 初始化IpcServer(RPC通信),DataNode-runDatanodeDaemon()中启动
initIpcServer(conf);
metrics = DataNodeMetrics.create(conf, getDisplayName());
metrics.getJvmMetrics().setPauseMonitor(pauseMonitor);
// 按照namespace(nameservice)、namenode的结构进行初始化
blockPoolManager = new BlockPoolManager(this);
blockPoolManager.refreshNamenodes(conf);
...// 略
}
//BlockPoolManager抽象了datanode提供的数据块存储服务。BlockPoolManager按照namespace(nameservice)、namenode结构组织。
//BlockPoolManager-refreshNamenodes()
//除了初始化过程主动调用,还可以由namespace通过datanode心跳过程下达刷新命令
void refreshNamenodes(Configuration conf)
throws IOException {
LOG.info("Refresh request received for nameservices: " + conf.get(DFSConfigKeys.DFS_NAMESERVICES));
Map<String, Map<String, InetSocketAddress>> newAddressMap = DFSUtil.getNNServiceRpcAddressesForCluster(conf);
synchronized (refreshNamenodesLock) {
doRefreshNamenodes(newAddressMap);
}
}
-------------------------------------------------------
private void doRefreshNamenodes(
Map<String, Map<String, InetSocketAddress>> addrMap) throws IOException {
assert Thread.holdsLock(refreshNamenodesLock);
Set<String> toRefresh = Sets.newLinkedHashSet();
Set<String> toAdd = Sets.newLinkedHashSet();
Set<String> toRemove;
synchronized (this) {
// Step 1. For each of the new nameservices, figure out whether
// it's an update of the set of NNs for an existing NS,
// or an entirely new nameservice.
for (String nameserviceId : addrMap.keySet()) {
if (bpByNameserviceId.containsKey(nameserviceId)) {
toRefresh.add(nameserviceId);
} else {
toAdd.add(nameserviceId);
}
}
...// 略
// Step 2. Start new nameservices
if (!toAdd.isEmpty()) {
LOG.info("Starting BPOfferServices for nameservices: " + Joiner.on(",").useForNull("<default>").join(toAdd));
for (String nsToAdd : toAdd) {
ArrayList<InetSocketAddress> addrs = Lists.newArrayList(addrMap.get(nsToAdd).values());
// 为每个namespace创建对应的BPOfferService
BPOfferService bpos = createBPOS(addrs);
bpByNameserviceId.put(nsToAdd, bpos);
offerServices.add(bpos);
}
}
// 然后通过startAll启动所有BPOfferService
startAll();
}
...// 略
}
------------------------------------------------
protected BPOfferService createBPOS(List<InetSocketAddress> nnAddrs) {
return new BPOfferService(nnAddrs, dn);
}
BPOfferService(List<InetSocketAddress> nnAddrs, DataNode dn) {
Preconditions.checkArgument(!nnAddrs.isEmpty(), "Must pass at least one NN.");
this.dn = dn;
for (InetSocketAddress addr : nnAddrs) {
this.bpServices.add(new BPServiceActor(addr, this));
}
}
--------------------------------------------
//BlockPoolManager#startAll()启动所有BPOfferService(实际是启动所有BPServiceActor)。
synchronized void startAll() throws IOException {
try {
UserGroupInformation.getLoginUser().doAs(
new PrivilegedExceptionAction<Object>() {
@Override
public Object run() throws Exception {
for (BPOfferService bpos : offerServices) {
bpos.start();
}
return null;
}
}
);
}
catch (InterruptedException ex) {
IOException ioe = new IOException();
ioe.initCause(ex.getCause());
throw ioe;
}
}
-------------------------------------------------------
//在datanode启动的主流程中,启动了多种工作线程,包括InfoServer、JVMPauseMonitor、BPServiceActor等。其中,最重要的是BPServiceActor线程,真正代表datanode与namenode通信的正是BPServiceActor线程。
//DataNode--initBlockPool():
/**
* One of the Block Pools has successfully connected to its NN.
* This initializes the local storage for that block pool,
* checks consistency of the NN's cluster ID, etc.
*
* If this is the first block pool to register, this also initializes
* the datanode-scoped storage.
*
* @param bpos Block pool offer service
* @throws IOException if the NN is inconsistent with the local storage.
*/
void initBlockPool(BPOfferService bpos) throws IOException {
...// 略
// 将blockpool注册到BlockPoolManager
blockPoolManager.addBlockPool(bpos);
// 初步初始化存储结构
initStorage(nsInfo);
...// 检查磁盘损坏
// 启动扫描器
initPeriodicScanners(conf);
// 将blockpool添加到FsDatasetIpml,并继续初始化存储结构
data.addBlockPool(nsInfo.getBlockPoolID(), conf);
}
NameNode如何支撑高并发访问(双缓冲机制)
高并发访问NameNode会遇到什么样的问题:
经过学习HDFS的元数据管理机制,Client每次请求NameNode修改一条元数据(比如说申请上传一个文件,都要写一条edits log,包括两个步骤:
- 写入本地磁盘--edits文件
- 通过网络传输给JournalNodes集群(Hadoop HA集群--结合zookeeper来学习)。
高并发的难点主要在于数据的多线程安全以及每个操作效率。
对于多线程安全:
NameNode在写edits log时几个原则:
- 写入数据到edits_log必须保证每条edits都有一个全局顺序递增的transactionId(简称为txid),这样才可以标识出来一条一条的edits的先后顺序。
- 如果要保证每条edits的txid都是递增的,就必须得加同步锁。也就是每个线程修改了元数据,要写一条edits 的时候,都必须按顺序排队获取锁后,才能生成一个递增的txid,代表这次要写的edits的序号。
产生的问题:
如果每次都是在一个加锁的代码块里,生成txid,然后写磁盘文件edits log,这种既有同步锁又有写磁盘操作非常耗时。
HDFS优化解决方案
问题产生的原因主要是在于,写edits时串行化排队生成自增txid + 写磁盘操作费时,
HDFS的解决方案
- 串行化:使用分段锁
- 写磁盘:使用双缓冲
分段加锁机制
首先各个线程依次第一次获取锁,生成顺序递增的txid,然后将edits写入内存双缓冲的区域1,接着就立马第一次释放锁了。趁着这个空隙,后面的线程就可以再次立马第一次获取锁,然后立即写自己的edits到内存缓冲。
双缓冲机制
程序中将会开辟两份一模一样的内存空间,一个为bufCurrent,产生的数据会直接写入到这个bufCurrent,而另一个叫bufReady,在bufCurrent数据写入(达到一定标准)后,两片内存就会exchange(交换)。直接交换双缓冲的区域1和区域2。保证接收客户端写入数据请求的都是操作内存而不是同步写磁盘。
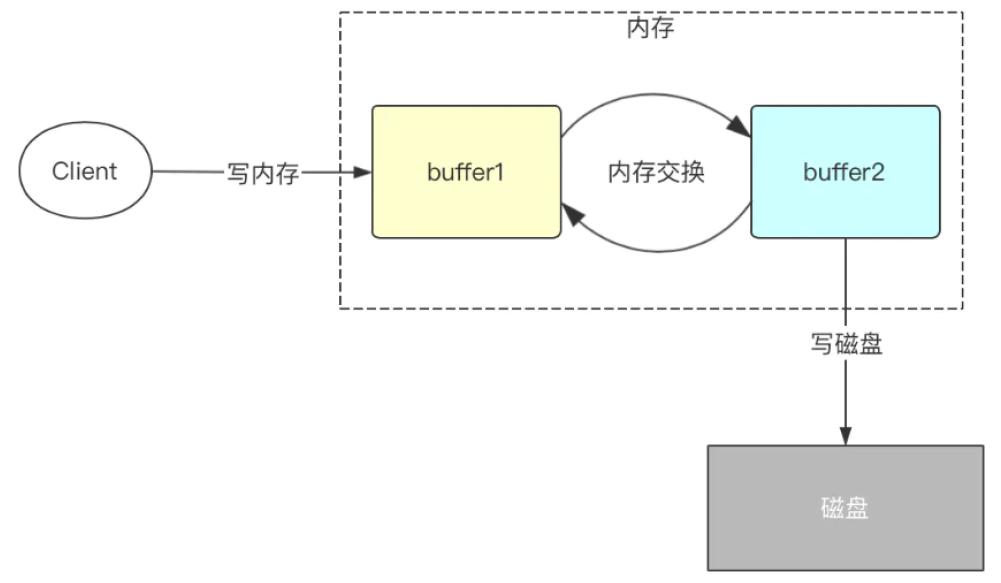
双缓冲源码分析 找到FsEditLog.java
...
void logEdit(final FSEditLogOp op) {
Boolean needsSync = false;
//是否同步的标识
synchronized (this) {
//
assert isOpenForWrite() : "bad state: " + state;
// wait if an automatic sync is scheduled 如果当前操作被其它线程调度,则等待1s钟
waitIfAutoSyncScheduled();
// check if it is time to schedule an automatic sync
needsSync = doEditTransaction(op);
if (needsSync) {
isAutoSyncScheduled = true;
//标识bufCurrent满了,进行双缓冲刷写
}
}
// Sync the log if an automatic sync is required.
if (needsSync) {
logSync();
//将缓冲区数据刷写到磁盘
}
}
...