分布式链路追踪技术适⽤场景(问题场景)
- 场景描述
为了⽀撑⽇益增⻓的庞⼤业务量,我们会使⽤微服务架构设计我们的系统,使得我们的系统不仅能够通过集群部署抵挡流量的冲击,⼜能根据业务进⾏灵活的扩展。
那么,在微服务架构下,⼀次请求少则经过三四次服务调⽤完成,多则跨越⼏⼗个甚⾄是上百个服务节点。那么问题接踵⽽来:
1)如何动态展示服务的调⽤链路?(⽐如A服务调⽤了哪些其他的服务---依赖关系)
2)如何分析服务调⽤链路中的瓶颈节点并对其进⾏调优?(⽐如A—>B—>C,C服务处理时间特别⻓)
3)如何快速进⾏服务链路的故障发现?
这就是分布式链路追踪技术存在的⽬的和意义 - 分布式链路追踪技术
如果我们在⼀个请求的调⽤处理过程中,在各个链路节点都能够记录下⽇志,并最终将⽇志进⾏集中可视化展示,那么我们想监控调⽤链路中的⼀些指标就有希望了,⽐如,请求到达哪个服务实例?请求被处理的状态怎样?处理耗时怎样?这些都能够分析出来了...
分布式环境下基于这种想法实现的监控技术就是就是分布式链路追踪(全链路追踪)。 - 市场上的分布式链路追踪⽅案
分布式链路追踪技术已经成熟,产品也不少,国内外都有,⽐如:
Spring Cloud Sleuth + Twitter Zipkin
阿⾥巴巴的“鹰眼”
⼤众点评的“CAT”
美团的“Mtrace”
京东的“Hydra”
新浪的“Watchman”
Apache Skywalking
分布式链路追踪技术核⼼思想
本质:记录⽇志,作为⼀个完整的技术,分布式链路追踪也有⾃⼰的理论和概念
微服务架构中,针对请求处理的调⽤链可以展现为⼀棵树,示意如下:
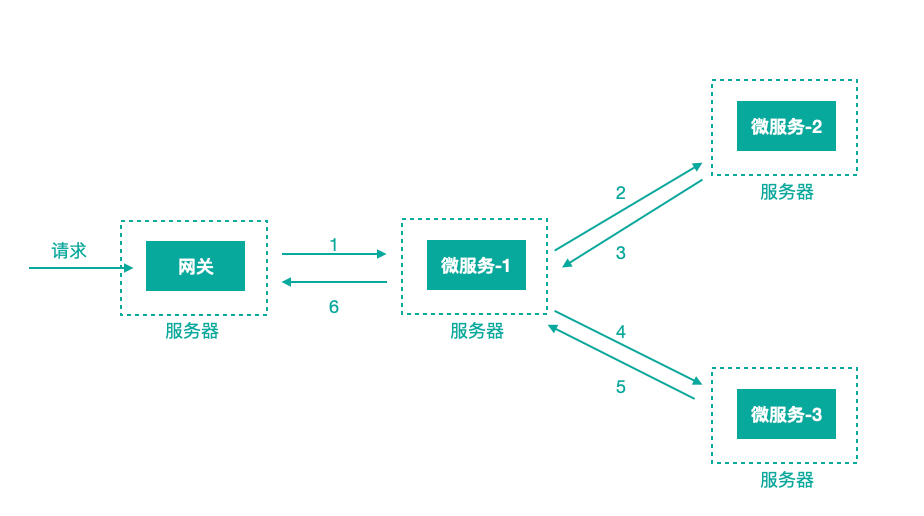
上图描述了⼀个常⻅的调⽤场景,⼀个请求通过⽹关服务路由到下游的微服务-1,然后微服务-1调⽤微服务-2,拿到结果后再调⽤微服务-3,最后组合微服务-2和微服务-3的结果,通过⽹关返回给⽤户
为了追踪整个调⽤链路,肯定需要记录⽇志,⽇志记录是基础,在此之上肯定有⼀些理论概念,当下主流的的分布式链路追踪技术/系统所基于的理念都来⾃于Google的⼀篇论⽂《Dapper, a Large-Scale Distributed Systems Tracing Infrastructure》,还以前⾯的服务调⽤来说这⾥⾯涉及到的核⼼理念:
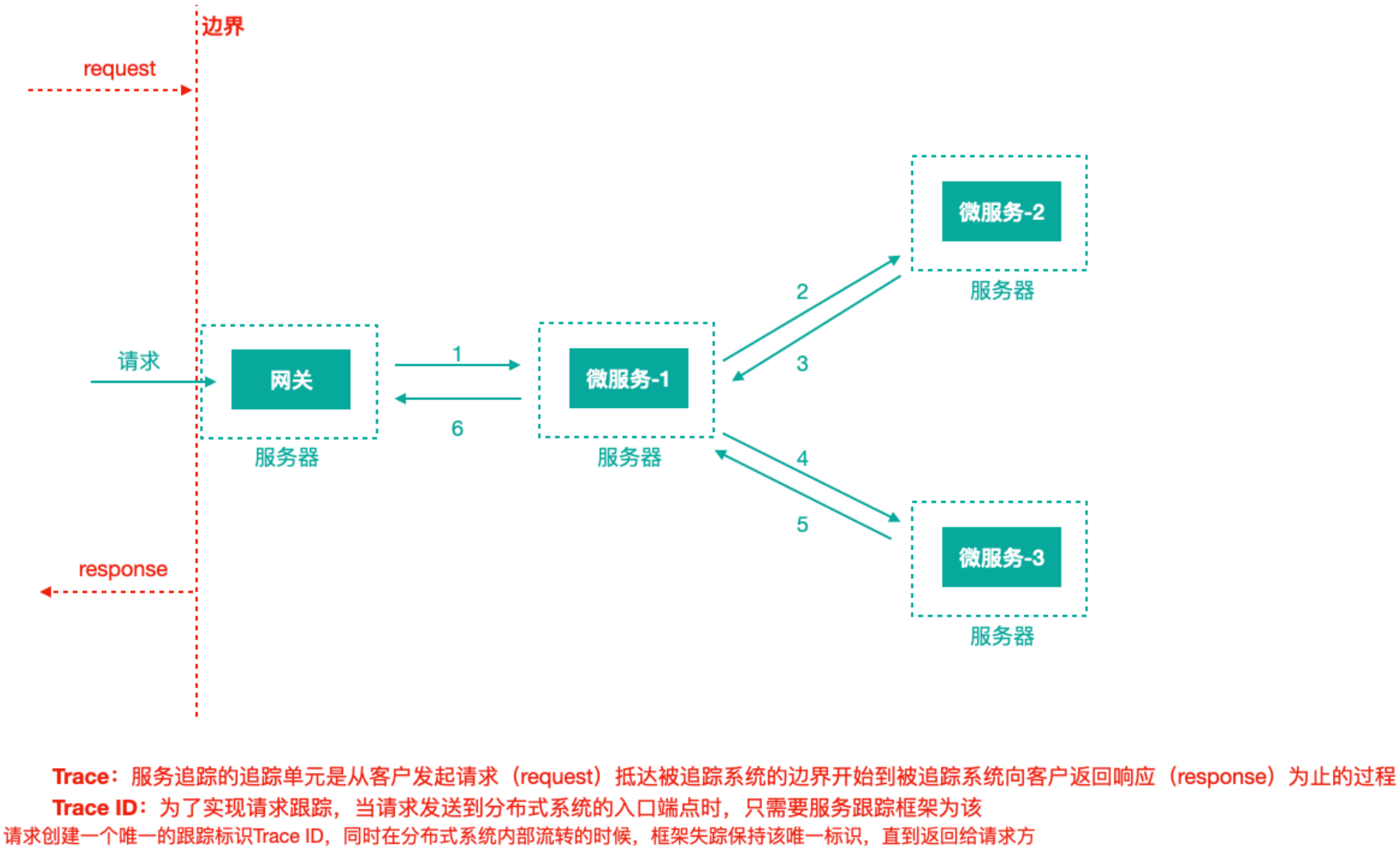
上图标识⼀个请求链路,⼀条链路通过TraceId唯⼀标识,span标识发起的请求信息,各span通过parrentId关联起来
Trace:服务追踪的追踪单元是从客户发起请求(request)抵达被追踪系统的边界开始,到被追踪系统向客户返回响应(response)为⽌的过程
Trace ID:为了实现请求跟踪,当请求发送到分布式系统的⼊⼝端点时,只需要服务跟踪框架为该请求创建⼀个唯⼀的跟踪标识Trace ID,同时在分布式系统内部流转的时候,框架失踪保持该唯⼀标识,直到返回给请求⽅
⼀个Trace由⼀个或者多个Span组成,每⼀个Span都有⼀个SpanId,Span中会记录TraceId,同时还有⼀个叫做ParentId,指向了另外⼀个Span的SpanId,表明⽗⼦关系,其实本质表达了依赖关系
Span ID:为了统计各处理单元的时间延迟,当请求到达各个服务组件时,也是通过⼀个唯⼀标识Span ID来标记它的开始,具体过程以及结束。对每⼀个Span来说,它必须有开始和结束两个节点,通过记录开始Span和结束Span的时间戳,就能统计出该Span的时间延迟,除了时间戳记录之外,它还可以包含
⼀些其他元数据,⽐如时间名称、请求信息等。
每⼀个Span都会有⼀个唯⼀跟踪标识 Span ID,若⼲个有序的 span 就组成了⼀个 trace。
Span可以认为是⼀个⽇志数据结构,在⼀些特殊的时机点会记录了⼀些⽇志信息,⽐如有时间戳、spanId、TraceId,parentIde等,Span中也抽象出了另外⼀个概念,叫做事件,核⼼事件如下
- CS :client send/start 客户端/消费者发出⼀个请求,描述的是⼀个span开始
- SR: server received/start 服务端/⽣产者接收请求 SR-CS属于请求发送的⽹络延迟
- SS: server send/finish 服务端/⽣产者发送应答 SS-SR属于服务端消耗时间
- CR:client received/finished 客户端/消费者接收应答 CR-SS表示回复需要的时间(响应的⽹络延迟)
Spring Cloud Sleuth (追踪服务框架)可以追踪服务之间的调⽤,Sleuth可以记录⼀个服务请求经过哪些服务、服务处理时⻓等,根据这些,我们能够理清各微服务间的调⽤关系及进⾏问题追踪分析。
- 耗时分析:通过 Sleuth 了解采样请求的耗时,分析服务性能问题(哪些服务调⽤⽐较耗时)
- 链路优化:发现频繁调⽤的服务,针对性优化等
Sleuth就是通过记录⽇志的⽅式来记录踪迹数据的
我们往往把Spring Cloud Sleuth 和 Zipkin ⼀起使⽤,把 Sleuth 的数据信息发送给 Zipkin 进⾏聚合,利⽤ Zipkin 存储并展示数据。
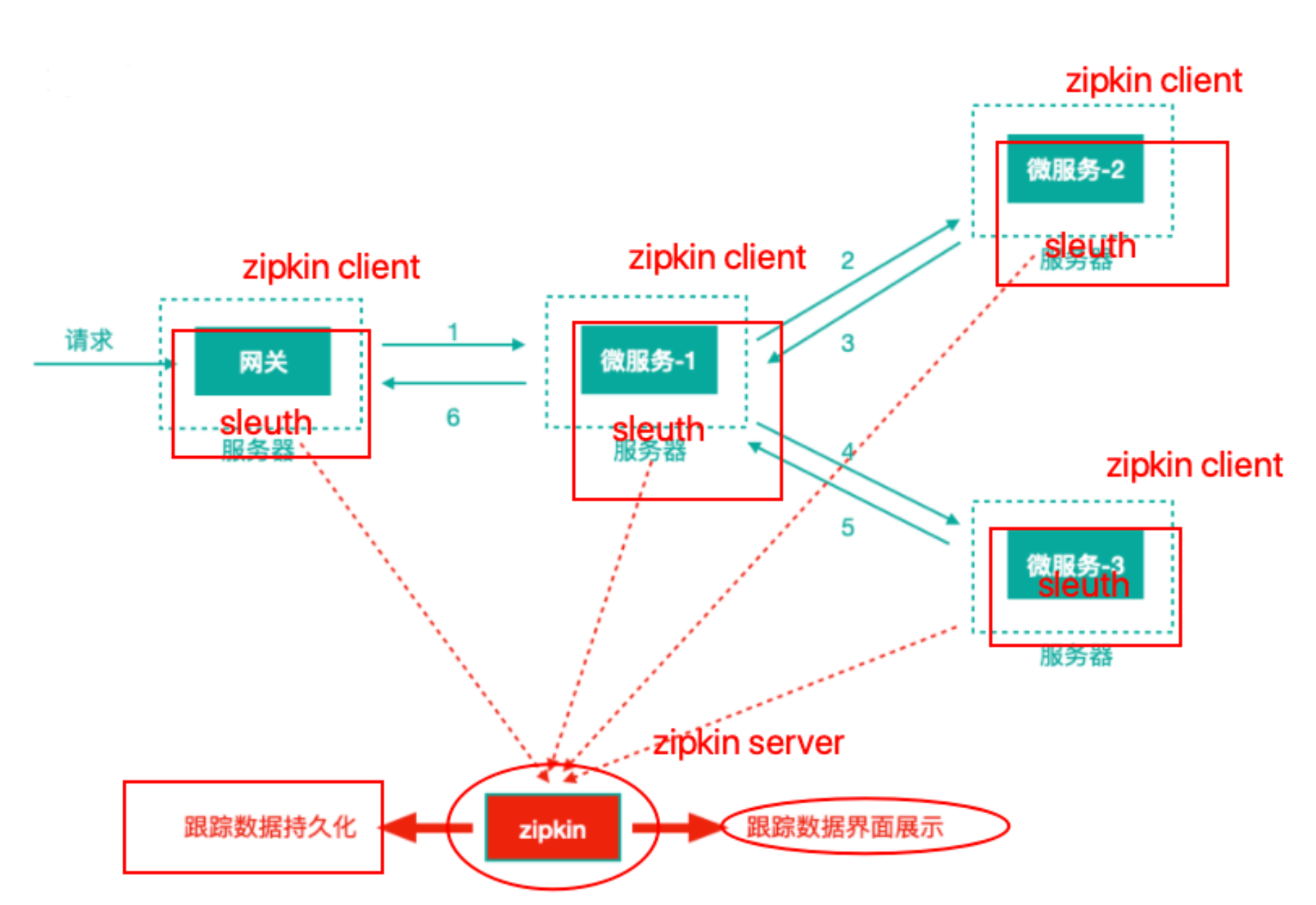
Sleuth + Zipkin
- 每⼀个需要被追踪踪迹的微服务⼯程都引⼊依赖坐标
<!--链路追踪-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-sleuth</artifactId>
</dependency>
- 每⼀个微服务都修改application.yml配置⽂件,添加⽇志级别
#分布式链路追踪
logging:
level:
org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet: debug
org.springframework.cloud.sleuth: debug
请求到来时,我们在控制台可以观察到 Sleuth 输出的⽇志(全局 TraceId、SpanId等)。

这样的⽇志⾸先不容易阅读观察,另外⽇志分散在各个微服务服务器上,接下来使⽤zipkin统⼀聚合轨迹⽇志并进⾏存储展示。
3. 结合 Zipkin 展示追踪数据
Zipkin包括Zipkin Server和Zipkin Client两部分,Zipkin Server是⼀个单独的服务,Zipkin Client就是具体的微服务。
- Zipkin Server 构建
pom.xml
<!--zipkin-server的依赖坐标-->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.zipkin.java</groupId>
<artifactId>zipkin-server</artifactId>
<version>2.12.3</version>
<exclusions>
<!--排除掉log4j2的传递依赖,避免和springboot依赖的⽇志组件冲突-->
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-log4j2</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<!--zipkin-server ui界⾯依赖坐标-->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.zipkin.java</groupId>
<artifactId>zipkin-autoconfigure-ui</artifactId>
<version>2.12.3</version>
</dependency>
⼊⼝启动类添加@EnableZipkinServer注解,用于开启Zipkin Server功能
application.yml
server:
port: 9411
management:
metrics:
web:
server:
# 关闭⾃动检测请求
auto-time-requests: false
- Zipkin Client构建(在具体微服务中修改)
pom中添加zipkin依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-zipkin</artifactId>
</dependency>
application.yml中添加对zipkin server的引⽤
spring:
application:
name: service-consumer
zipkin:
# zipkin server的请求地址
base-url: http://127.0.0.1:9411
sender:
# web 客户端将踪迹⽇志数据通过⽹络请求的⽅式传送到服务端,另外还有配置
# kafka/rabbit 客户端将踪迹⽇志数据传递到mq进⾏中转
type: web
sleuth:
sampler:
# 采样率 1 代表100%全部采集 ,默认0.1 代表10% 的请求踪迹数据会被采集
# ⽣产环境下,请求量⾮常⼤,没有必要所有请求的踪迹数据都采集分析,对于⽹络包括server端压⼒都是⽐较⼤的,可以配置采样率采集⼀定⽐例的请求的踪迹数据进⾏分析即可
probability: 1
另外,对于log⽇志,依然保持开启debug状态
logging:
level:
org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet: debug
org.springframework.cloud.sleuth: debug
Zipkin server⻚⾯⽅便我们查看服务调⽤依赖关系及⼀些性能指标和异常信息
- 追踪数据Zipkin持久化到mysql(官方还支持elasticsearch、cassandra)
mysql中创建名称为zipkin的数据库,并执⾏如下sql语句(官⽅提供)
--
-- Copyright 2015-2019 The OpenZipkin Authors
--
-- Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except
-- in compliance with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
--
-- http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
--
-- Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License
-- is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express
-- or implied. See the License for the specific language governing permissions and limitations under
-- the License.
--
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS zipkin_spans (
`trace_id_high` BIGINT NOT NULL DEFAULT 0 COMMENT 'If non zero, this means the trace uses 128 bit traceIds instead of 64 bit',
`trace_id` BIGINT NOT NULL,
`id` BIGINT NOT NULL,
`name` VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
`remote_service_name` VARCHAR(255),
`parent_id` BIGINT,
`debug` BIT(1),
`start_ts` BIGINT COMMENT 'Span.timestamp(): epoch micros used for endTs query and to implement TTL',
`duration` BIGINT COMMENT 'Span.duration(): micros used for minDuration and maxDuration query',
PRIMARY KEY (`trace_id_high`, `trace_id`, `id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB ROW_FORMAT=COMPRESSED CHARACTER SET=utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci;
ALTER TABLE zipkin_spans ADD INDEX(`trace_id_high`, `trace_id`) COMMENT 'for getTracesByIds';
ALTER TABLE zipkin_spans ADD INDEX(`name`) COMMENT 'for getTraces and getSpanNames';
ALTER TABLE zipkin_spans ADD INDEX(`remote_service_name`) COMMENT 'for getTraces and getRemoteServiceNames';
ALTER TABLE zipkin_spans ADD INDEX(`start_ts`) COMMENT 'for getTraces ordering and range';
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS zipkin_annotations (
`trace_id_high` BIGINT NOT NULL DEFAULT 0 COMMENT 'If non zero, this means the trace uses 128 bit traceIds instead of 64 bit',
`trace_id` BIGINT NOT NULL COMMENT 'coincides with zipkin_spans.trace_id',
`span_id` BIGINT NOT NULL COMMENT 'coincides with zipkin_spans.id',
`a_key` VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL COMMENT 'BinaryAnnotation.key or Annotation.value if type == -1',
`a_value` BLOB COMMENT 'BinaryAnnotation.value(), which must be smaller than 64KB',
`a_type` INT NOT NULL COMMENT 'BinaryAnnotation.type() or -1 if Annotation',
`a_timestamp` BIGINT COMMENT 'Used to implement TTL; Annotation.timestamp or zipkin_spans.timestamp',
`endpoint_ipv4` INT COMMENT 'Null when Binary/Annotation.endpoint is null',
`endpoint_ipv6` BINARY(16) COMMENT 'Null when Binary/Annotation.endpoint is null, or no IPv6 address',
`endpoint_port` SMALLINT COMMENT 'Null when Binary/Annotation.endpoint is null',
`endpoint_service_name` VARCHAR(255) COMMENT 'Null when Binary/Annotation.endpoint is null'
) ENGINE=InnoDB ROW_FORMAT=COMPRESSED CHARACTER SET=utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci;
ALTER TABLE zipkin_annotations ADD UNIQUE KEY(`trace_id_high`, `trace_id`, `span_id`, `a_key`, `a_timestamp`) COMMENT 'Ignore insert on duplicate';
ALTER TABLE zipkin_annotations ADD INDEX(`trace_id_high`, `trace_id`, `span_id`) COMMENT 'for joining with zipkin_spans';
ALTER TABLE zipkin_annotations ADD INDEX(`trace_id_high`, `trace_id`) COMMENT 'for getTraces/ByIds';
ALTER TABLE zipkin_annotations ADD INDEX(`endpoint_service_name`) COMMENT 'for getTraces and getServiceNames';
ALTER TABLE zipkin_annotations ADD INDEX(`a_type`) COMMENT 'for getTraces and autocomplete values';
ALTER TABLE ADD INDEX(`a_key`) COMMENT 'for getTraces and autocomplete values';
ALTER TABLE zipkin_annotations ADD INDEX(`trace_id`, `span_id`, `a_key`) COMMENT 'for dependencies job';
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS zipkin_dependencies (
`day` DATE NOT NULL,
`parent` VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
`child` VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
`call_count` BIGINT,
`error_count` BIGINT,
PRIMARY KEY (`day`, `parent`, `child`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB ROW_FORMAT=COMPRESSED CHARACTER SET=utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci;
pom⽂件引⼊相关依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>io.zipkin.java</groupId>
<artifactId>zipkin-autoconfigure-storage-mysql</artifactId>
<version>2.12.3</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.1.10</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-tx</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId>
</dependency>
修改配置⽂件,添加如下内容
spring:
datasource:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/zipkin?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&useSSL=false&allowMultiQueries=true
username: root
password: 123456
druid:
initialSize: 10
minIdle: 10
maxActive: 30
maxWait: 50000
# 指定zipkin持久化介质为mysql
zipkin:
storage:
type: mysql
启动类中注⼊事务管理器
@Bean
public PlatformTransactionManager txManager(DataSource dataSource) {
return new DataSourceTransactionManager(dataSource);
}